#PanopticSegmentation #ComputerVison # OpenDataset #AI #InstanceSegmentation #SemanticSegmentation #auto-driving #healthcare #RemoteSensing #Agriculture #DigitalImageProcessing #SmartCities
Panoptic Segmentation unifies typically dense prediction tasks of semantic segmentation and instance segmentation into a holistic task, providing broader application and an essential step toward real-world vision systems.
In this article, we will talk about the advancements of use cases and applications of panoptic segmentation, especially auto-driving, healthcare, remote sensing, agriculture, digital imaging, and smart city. Also, the enabling open datasets and commercial datasets behind state-of-the-art models are summarized.
1. What is Panoptic Segmentation?
Computer Vision is an essential task as one of the most important area of artificial intelligence (AI), which require the machine to perceive environments and understand visual content as humans. Dense prediction tasks of computer vision, include image segmentation, instance segmentation, and panoptic segmentation. These dense prediction tasks, such as image classification, are more challenging than others because the machine needs to make pixel-level predictions.
Furthermore, these tasks transform an image into segments humans can easily understand or process. Panoptic Segmentation is a most valuable task, which requires both segmenting each instance and all stuff categories in a unified framework.
For more professional and detailed explanations of panoptic segmentation, please read:
Repost | Overview of Panoptic Segmentation — towards Real-World Computer Vision (Part.1)
2. Use cases and applications of panoptic segmentation
There are various real-world use cases and applications in which panoptic segmentation plays a significant role.
2.1 Autonomous driving
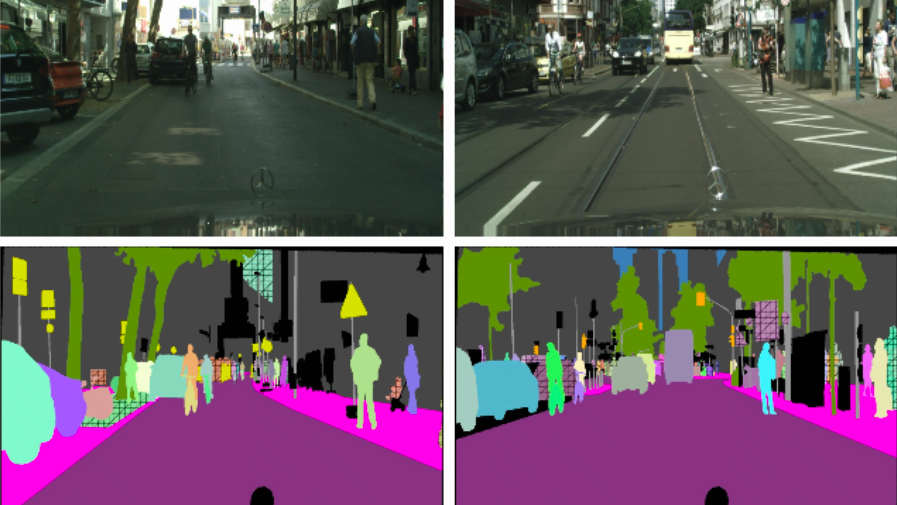
Panoramic segmentation is essential for establishing the safety and accuracy of self-driving vehicles.

With panoptic segmentation, the image and video can be accurately parsed for both semantic (where pixels indicate automobiles, pedestrians, and drivable space, respectively) and instance information (where pixels represent the same car vs. other car objects).
For more information, please click the link to read: Panoptic Segmentation enables Real-World Computer Vision in Autonomous Driving
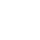
2.2 Healthcare
Since the progress of panoptic segmentation, great interest has been paid to using this task in the Healthcare industry, especially in life-saving fields such as medical imaging and helping visually impaired people to provide a holistic understanding of their surroundings.
To read more details, please click: Panoptic Segmentation enables Real-World Computer Vision in Healthcare Industries
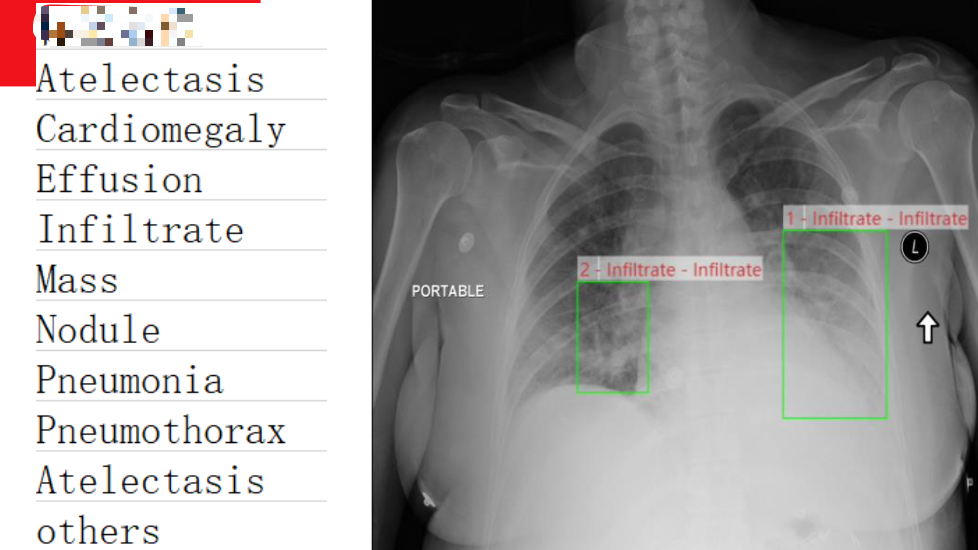
2.3 Remote Sensing
According to USGC, remote sensing is the process of detecting and monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by measuring its reflected and emitted radiation at a distance (typically from satellite or aircraft). Special cameras collect remotely sensed images, which help researchers “sense” things about the Earth.[1]
In simple words, remote sensing is a process of gathering information regarding some objects or phenomena on the earth without touching them. It’s related to acquiring data by utilizing satellites, radars, unmanned aerial vehicles, various sensors, and more.
For instance, estimating forest conditions, weather forecasting, optimizing transportation, detecting changes in land cover and land use, detecting points of interest, optimizing transportation, predicting hazardous events, etc.
All of these are possible to rely on the data collected from remote sensing missions.
Under the circumstance, panoptic segmentation can be used to boost the performance of road condition monitoring or urban planning. Panoptic segmentation can provide extra background and foreground information for precise remote sensing detection. Some methods utilize this task to provide more comprehensive information.
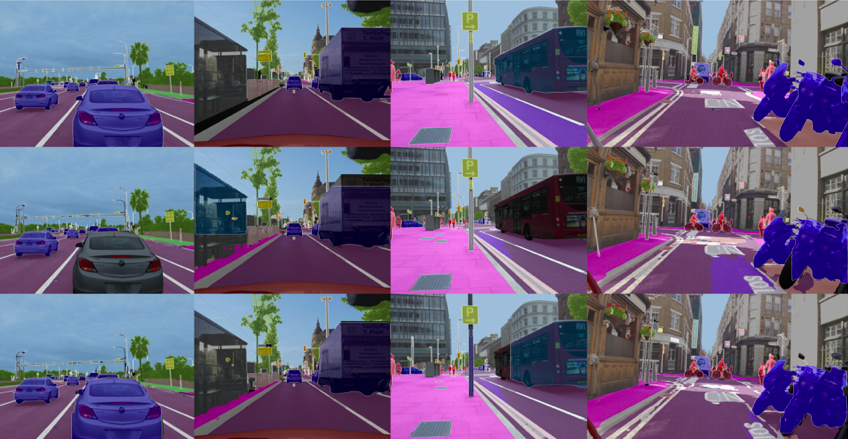
For instance, [2] proposes a new framework to use panoptic segmentation for the scale problem in UAV images, i.e., The vast target scene and small UAV target led to a lack of foreground targets in the segmentation findings and low segmentation mask quality. Typically, a deformable convolution is added to the feature extraction network to improve its ability to extract features.
Moreover, the MaskIoU module is developed and incorporated into the instance segmentation branch to improve the overall quality of the foreground target mask. In addition, a collection of UAV-collected data is arranged into the UAV-OUC panoptic segmentation dataset for testing and validating panoptic segmentation models in aerial imagery.
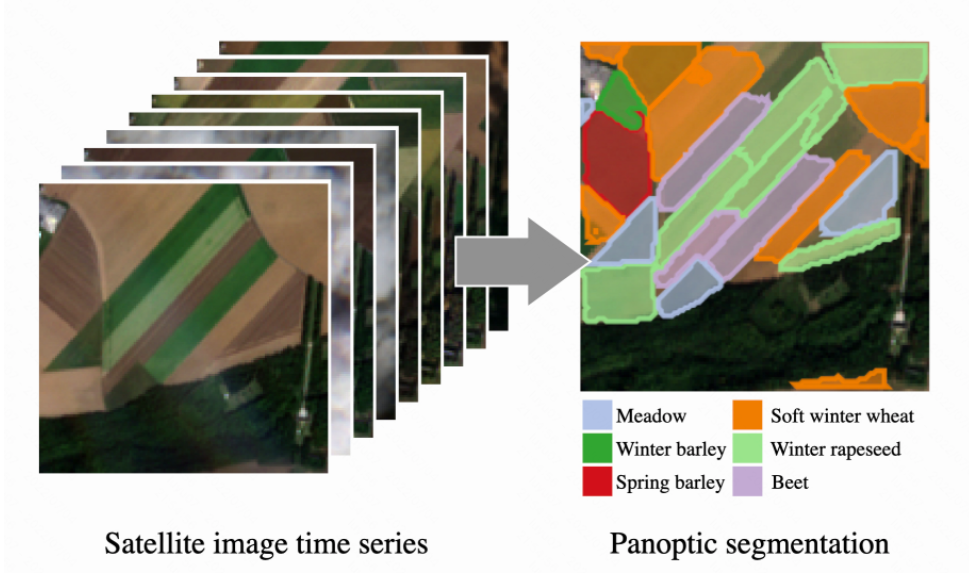
(Fig6 Results of panoptic segmentation on UAV tasks)
2.4 Agriculture
Panoptic segmentation is also used in the agriculture area.
Accordingly, Behavioral research of pigs can be greatly simplified if automatic recognition systems are used. Systems based on computer vision in particular have the advantage that they allow an evaluation without affecting the normal behavior of the animals.[3]
Such as, in [4], they use panoptic segmentation to analyze the behavior of pigs. They follow the relatively new definition of panoptic segmentation and aim at the pixel-accurate segmentation of the individual pigs instead of bounding boxes or key points.
Panoptic segmentation provides more information that can be extracted from the segmentation of the weight or size of animals. The method is tested on a specially created data set with 1000 hand-labeled images and achieves detection rates of around 95% (F1 Score) despite disturbances such as occlusions and dirty lenses.
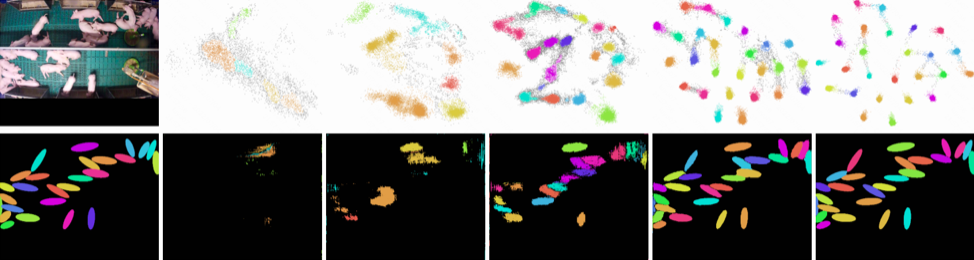
(Fig 7 panoptic segmentation for pig behavior)
Nowadays, as the demand for taking pictures with smartphones becomes much more common, smartphones are equipped with HD cameras.
Panoptic segmentation unifies scene-level and subject-level understanding by predicting two attribues for each pixel: a categorical label and a subject label.
It means that panoptic segmentation is able to leverage its ability to separate things from stuff. So smartphone cameras can create multiple effects, such as Auto-focus, Photo-manipulation, Multi-Object Panoptic Tracking, Portrait mode, background blur, etc.

(Photo by Antoine Beauvillain on Unsplash)
2.5 Smart Cities
Now, think of the importance of panoptic segmentation for autonomous self-driving and image to expand it across an entire city.
With the help of state-of-the-art, AI technologies will become more and more ’smart’, from city monitoring and management to optimization of all areas from utilities, coving defense and security, healthcare, education, and our day-to-day life, etc.
We have reason to believe that panoptic segmentation can also offer an accurate and efficient model for smart cities to rely on.

(Photo by Marc-Olivier Jodoin on Unsplash)
3. Related open & commercial datasets
AI is driven by data, not code. Here are several open datasets and commercial datasets as follows.
High-Quality Panoptic Segmentation Datasets
Reference List:
[1] https://www.usgs.gov/faqs/what-remote-sensing-and-what-it-used
[2] Panoptic segmentation of UAV images with deformable convolution network and mask scoring
[3] https://deepai.org/publication/panoptic-instance-segmentation-on-pigs
[4] Panoptic Instance Segmentation on Pigs